
Sample Paper from Experts on Principles of Dimensional Modeling
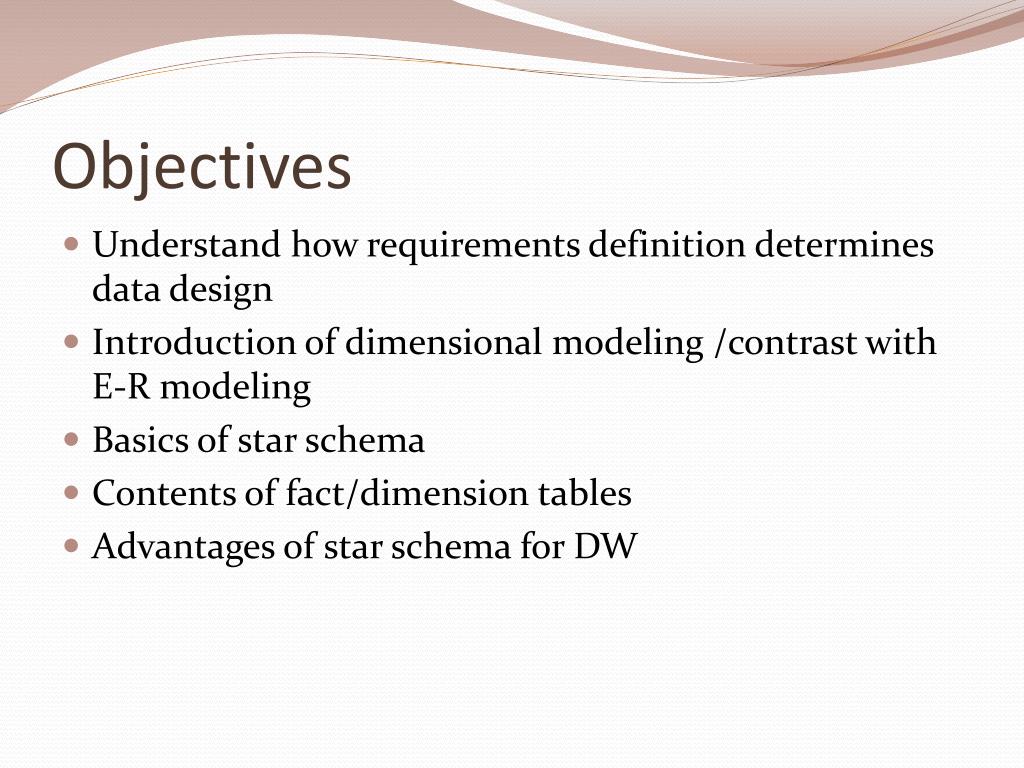
Dimensional Modeling is a favorite modeling technique in data warehousing. DM is a logical design technique that seeks to present the data in a standard, intuitive framework that allows for high-performance access. It is inherently dimensional, and it adheres to a discipline that uses the relational model with some important restrictions · Steps to Create Dimensional Data Modelling: Step Identifying the business objective – The first step is to identify the business objective. Sales, HR, Marketing, etc. are some examples as per the need of the organization. Since it is the most important step of Data Modelling the selection of business objective also depends on the quality of data available for · This chapter contains sections titled: Chapter Objectives From Requirements to Data Design The Star Schema Star Schema Keys Advantages of the Star Schema Star Schema: Examples Chapter S
Related Articles
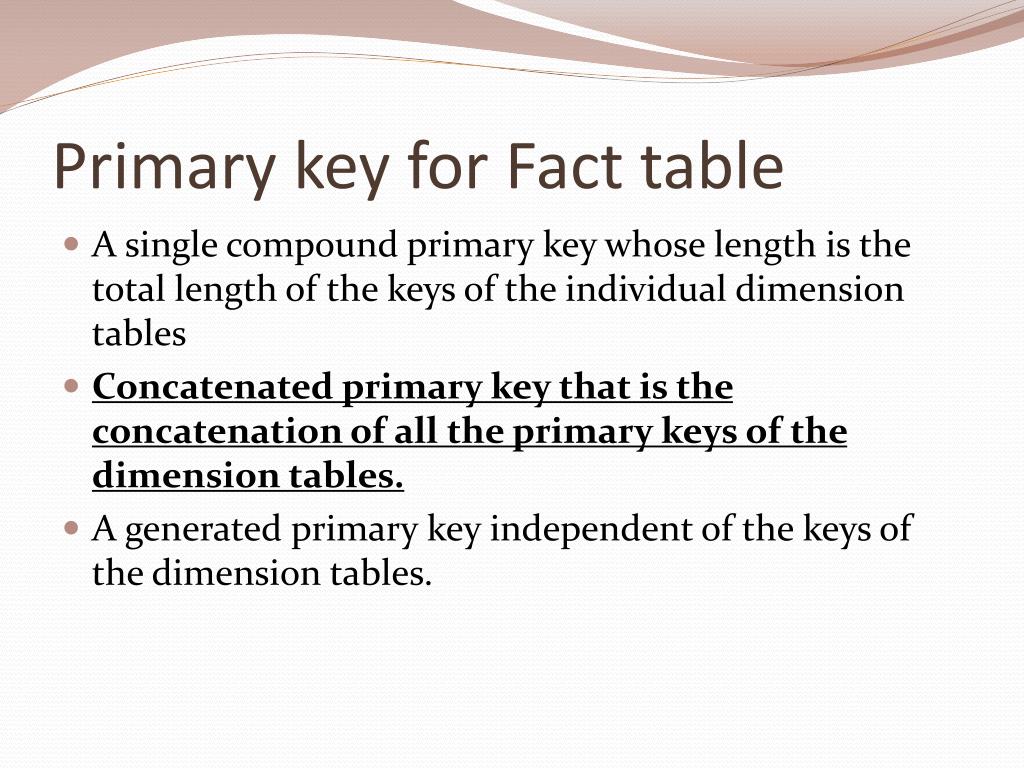
Slowly Changing Dimension Techniques. Type 0: Retain original; Type 1: Overwrite; Type 2: Add new row; Type 3: Add new attribute; Type 4: Add mini-dimension; Type 5: Add mini-dimension and Type 1 outrigger; Type 6: Add Type 1 attributes to Type 2 dimension; Type 7: Dual Type 1 and Type 2 dimensions; Dimension Hierarchy Techniques. Fixed depth positional hierarchies CHAPTER 10 PRINCIPLES OF DIMENSIONAL MODELING CHAPTER OBJECTIVES Clearly unde rstand how the requirements definition determines data design Introduce dimensional modeling and contrast it with entity-relationship modeling Review the basics of the STAR schema Find out what is inside the fact table and inside the dimension tables · Steps to Create Dimensional Data Modelling: Step Identifying the business objective – The first step is to identify the business objective. Sales, HR, Marketing, etc. are some examples as per the need of the organization. Since it is the most important step of Data Modelling the selection of business objective also depends on the quality of data available for

Elements involved in Dimensional Modeling
CHAPTER 10 PRINCIPLES OF DIMENSIONAL MODELING CHAPTER OBJECTIVES Clearly unde rstand how the requirements definition determines data design Introduce dimensional modeling and contrast it with entity-relationship modeling Review the basics of the STAR schema Find out what is inside the fact table and inside the dimension tables · This chapter contains sections titled: Chapter Objectives From Requirements to Data Design The Star Schema Star Schema Keys Advantages of the Star Schema Star Schema: Examples Chapter S Slowly Changing Dimension Techniques. Type 0: Retain original; Type 1: Overwrite; Type 2: Add new row; Type 3: Add new attribute; Type 4: Add mini-dimension; Type 5: Add mini-dimension and Type 1 outrigger; Type 6: Add Type 1 attributes to Type 2 dimension; Type 7: Dual Type 1 and Type 2 dimensions; Dimension Hierarchy Techniques. Fixed depth positional hierarchies
Basic Fact Table Techniques
· Steps to Create Dimensional Data Modelling: Step Identifying the business objective – The first step is to identify the business objective. Sales, HR, Marketing, etc. are some examples as per the need of the organization. Since it is the most important step of Data Modelling the selection of business objective also depends on the quality of data available for CHAPTER 10 PRINCIPLES OF DIMENSIONAL MODELING CHAPTER OBJECTIVES Clearly unde rstand how the requirements definition determines data design Introduce dimensional modeling and contrast it with entity-relationship modeling Review the basics of the STAR schema Find out what is inside the fact table and inside the dimension tables Slowly Changing Dimension Techniques. Type 0: Retain original; Type 1: Overwrite; Type 2: Add new row; Type 3: Add new attribute; Type 4: Add mini-dimension; Type 5: Add mini-dimension and Type 1 outrigger; Type 6: Add Type 1 attributes to Type 2 dimension; Type 7: Dual Type 1 and Type 2 dimensions; Dimension Hierarchy Techniques. Fixed depth positional hierarchies

Fundamental Concepts
· This chapter contains sections titled: Chapter Objectives From Requirements to Data Design The Star Schema Star Schema Keys Advantages of the Star Schema Star Schema: Examples Chapter S · Steps to Create Dimensional Data Modelling: Step Identifying the business objective – The first step is to identify the business objective. Sales, HR, Marketing, etc. are some examples as per the need of the organization. Since it is the most important step of Data Modelling the selection of business objective also depends on the quality of data available for CHAPTER 10 PRINCIPLES OF DIMENSIONAL MODELING CHAPTER OBJECTIVES Clearly unde rstand how the requirements definition determines data design Introduce dimensional modeling and contrast it with entity-relationship modeling Review the basics of the STAR schema Find out what is inside the fact table and inside the dimension tables
No comments:
Post a Comment